Browser automation has completely changed how teams test web applications and tackle repetitive tasks. The right tool can save hours, reduce mistakes, and streamline workflows. But with so many options, finding the best browser automation tool can feel overwhelming.
Overview
Popular Browser Automation Tools in 2026
- BrowserStack Automate delivers real-device, scalable browser automation with fast parallel execution.
- Selenium provides a flexible open-source framework for code-based, cross-browser automation.
- Puppeteer offers high-speed Chrome and Chromium automation with powerful browser APIs.
- Playwright enables reliable multi-browser automation across Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit.
- Cypress supports developer-friendly front-end testing with in-browser execution and time-travel debugging.
- Browserflow allows no-code browser workflow automation for simple repetitive tasks.
- UI Vision performs visual and UI-based automation with built-in macro recording inside the browser.
- Browser Automation Studio (BAS) provides a drag-and-drop builder for multi-threaded browser bots and scripting.
- TagUI enables open-source, cross-platform RPA and browser automation with human-readable syntax.
- Axiom.ai offers no-code Chrome automation for form filling, scraping, and routine web tasks.
- UiPath Studio Web delivers enterprise-grade browser automation integrated into full RPA workflows.
- Bardeen automates SaaS and productivity workflows directly inside the browser using a lightweight extension.
- Microsoft Power Automate supports broad automation with UI flows for web and enterprise app automation.
Drawing on my experience and expertise in this field, I have handpicked 13 top tools and highlighted their key features. Explore each option to see how it fits your workflow and project needs.
What is Browser Automation?
Browser automation is the process of using software to programmatically control web browsers, replicating human actions such as clicking, typing, navigating, and validating results without manual input.
While scripts define these actions, executing them reliably across different environments requires robust infrastructure. This is where platforms like BrowserStack Automate come in. They allow teams to run automated tasks ranging from QA and regression testing to data extraction. These tasks can be executed across thousands of real device and browser combinations instantly.
Importance of Browser Automation Tools
Browser automation tools serve critical needs in more than one way, from faster test cycles to accurate validation across browsers. Here are four reasons that define their importance:
- Cut manual test time and reduce repetitive effort across web workflows.
- Detects UI defects early with stable, repeatable actions across browsers and versions.
- Support continuous testing pipelines with consistent environments and predictable outputs.
- Handle large regression suites with parallel execution and broad device coverage.
Also Read:Bug vs Defect: Core Differences
In addition to these major advantages, browser automation tools also help maintain test accuracy during UI changes, support secure validation of complex user flows, and reduce flakiness caused by local system limits.
Popular Browser Automation Tools in 2026
Browser automation has evolved rapidly, and 2026 brings a new generation of tools built for speed, scale, and reliability. Here are the most widely used browser automation tools shaping modern testing workflows.
1. BrowserStack Automate
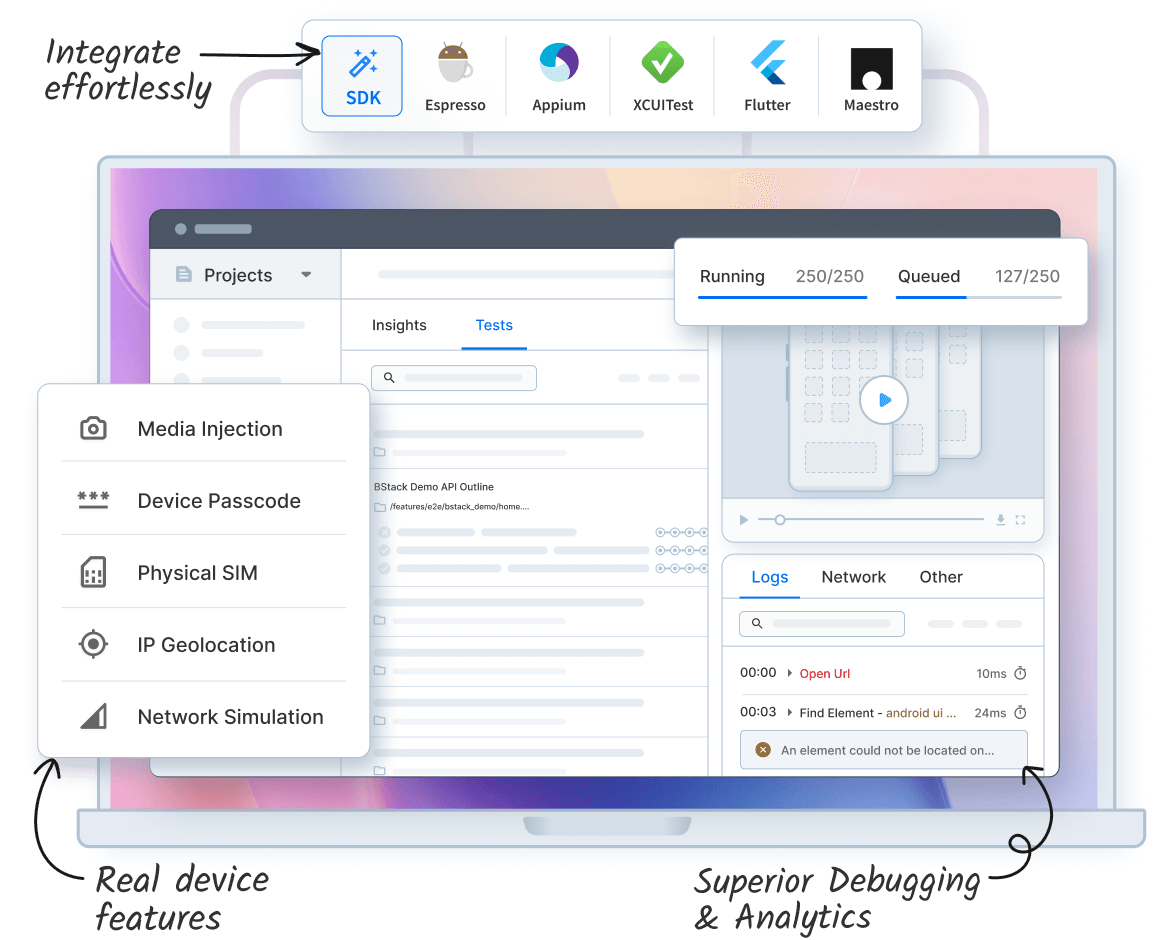
BrowserStack Automate provides cloud-based browser automation on real devices and real browsers. It supports fast execution, stable test runs, and strong debugging data across global device grids. The platform removes infrastructure setup and helps teams run tests at scale with predictable performance.
Best for: Teams that need stable cross browser automation on real devices with fast parallel execution.
Key Features & Benefits
- Massive real-device and browser coverage: Access 3,500+ real desktop and mobile browser-OS combinations, including the latest versions and day-0 device releases.
- High parallel execution: Run hundreds or thousands of tests simultaneously to cut build times and accelerate release cycles.
- No code changes needed: Plug in existing Selenium, Playwright, Cypress, or Puppeteer test suites using ready-to-use SDKs.
- Deep debugging insights: Get videos, screenshots, network logs, console output, and unified dashboards for rapid root-cause analysis.
- AI-powered test intelligence: Includes self-healing for broken locators, smart failure categorization, flakiness detection, and impact-based test selection to speed up CI pipelines.
- Cross-Browser Automation: Enables reliable, parallel test execution across thousands of real browsers and devices.’#139;
- Local testing support: Securely test internal, staging, and development environments behind firewalls.
- Seamless integrations: Connect with 150+ tools-CI/CD systems, bug trackers, and project platforms (GitHub, Jenkins, Jira, CircleCI, etc.) to fit into existing workflows.
- Enterprise-grade security: Every test runs on isolated, tamper-proof devices or VMs, wiped clean after each session.
- Support for complex real-world scenarios: Validate network conditions, payment flows, geolocation, and localization on real devices.
Why Choose BrowserStack Automate?
- Instant access to a large, always-updated library of real devices and browsers.
- Minimal maintenance with 24/7 availability and predictable performance.
- Comprehensive coverage and reliable execution that help teams ship faster with fewer regressions.
Pricing for Automate:
- BrowserStack Automate offers a free trial so teams can evaluate the platform quickly.
- Paid plans start at $99 per month, giving you access to real browsers without managing any infrastructure.
2. Selenium
Selenium is an open source browser automation framework that uses WebDriver to control browsers the same way a real user would. It supports multiple languages and works across major browsers. It includes different components: WebDriver for code-based automation, IDE for record/replay tests, and Grid for running tests across many environments.
Best for: Organizations and developers needing full control over browsers with flexible, code-based testing across environments.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Multi-language support: Lets testers write scripts in Java, Python, Ruby, JavaScript and more.
- Cross-browser compatibility: Works with Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge and other major browsers.
- Parallel and distributed tests (Grid): Enables running tests across machines to speed up large suites.
Verdict: Flexible and powerful browser automation tool for cross-browser tasks, but setup and maintenance can be complex.
3. Puppeteer
Puppeteer is a Node.js library that provides a high-level API to control Chrome as well as Firefox. It manages headless or headful browser sessions, enabling navigation, interaction, screenshots or PDF generation. It suits automation tasks where speed and direct browser control matter highly.
Best for: Developers or small teams aiming for fast automation tasks on Chromium or Chrome-based workflows.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Headless mode support: Enables fast automation runs without UI overhead for testing or scraping.
- Rich browser APIs: Allows screenshots, PDF generation, DOM queries, and performance tracing.
- Network interception & request control: Lets tests or scripts intercept requests, modify responses, or simulate network conditions.
Verdict: Fast and reliable Chrome automation tool, however it lacks full cross-browser support.
4. Playwright
Playwright is an open-source automation library created by Microsoft that offers a unified API for Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit browsers. It supports headless and headed modes, parallel runs, context isolation, network control and built-in test runner support. It aims to give stable, cross-browser automation for modern web applications.
Best for: Teams needing reliable automation across different browser engines with minimal flakiness.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Unified multi-browser API: One codebase can test on Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit.
- Automatic waits and reliable execution: Reduces timing issues by auto-handling element availability.
- Built-in test tooling: Supports parallel execution, retries, screenshots or video capturing, and context-based isolation.
Verdict: Stable multi-browser automation tool with rich features, yet real-device testing support is limited.
5. Cypress
Cypress is a JavaScript testing framework that runs inside the browser, offering deep insight into DOM state, network, and UI behavior. It emphasizes developer experience through live reloads, time-travel debugging, and fast feedback loops. It’s built for modern web apps and front-end testing scenarios.
Best for: Front-end teams who want quick, interactive testing with strong visibility into application state.
Key Features and Benefits:
- In-browser execution: Tests run inside a real browser session with access to DOM and network.
- Time travel debugger: Lets developers inspect each step to diagnose failures effectively.
- Easy setup for JS stacks: Provides quick start and integrates smoothly with modern front-end frameworks.
Verdict: Excellent front-end testing automation tool with live feedback, but supports fewer browsers and devices.
Must Read: How to perform Cypress Test Automation
6. Browserflow
Browserflow is a no-code, cloud-based automation tool that captures user workflows in the browser and converts them into automated tasks. It targets data entry, scraping, or repetitive admin tasks. It appeals to non-developers or teams that need simple browser automation without writing code.
Best for: Non technical users or business teams who want to automate routine browser tasks without scripting.
Key Features and Benefits:
- No-code workflow builder: Lets users record and replay browser steps visually.
- Cloud execution: Runs automation remotely without local setup.
- Web data extraction: Helps collect data from websites for reporting or CSV exports.
Verdict: Easy no-code automation tool for repetitive browser tasks, however it is not suitable for complex workflows.
7. UI Vision
UI Vision is a browser extension that combines DOM-based automation with image or visual recognition. It allows recording simple macros, validating UI visually, and automating tasks directly in the browser. It works without heavy environments and suits quick small-scale automation jobs.
Best for: Individuals or small teams needing quick visual automation or macro-based tasks in the browser.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Visual UI recognition: Detects layout changes via screenshots for visual validation.
- Macro record and replay: Captures user actions for reuse without coding.
- Local execution mode: Runs directly in the browser, no heavy setup needed.
Verdict: Quick visual and macro-based automation tool, but not ideal for large-scale or structured tests.
8. Browser Automation Studio (BAS)
Browser Automation Studio is a tool from Bablosoft that uses a Chrome engine emulation to automate web tasks with a drag-and-drop visual builder or custom scripts. It supports mouse/keyboard emulation, multithreading, HTTP client actions, captcha solving, fingerprint switching, and database integration.
Best for: Individuals or teams needing multi-threaded browser bots and automated workflows without complex setup.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Visual script builder: Lets users build browser flows via drag-and-drop instead of coding.
- Multi-thread and HTTP client support: Executes many tasks in parallel with fast HTTP calls.
- Captcha & fingerprint handling: Integrates with services to solve captchas and manage browser fingerprint for anonymity or multi-account workflows.
Verdict: Strong for bot creation and parallel runs; lacks structured QA testing features.
Also Read: AI Automation and Testing
9. TagUI
TagUI is an open source RPA and browser automation tool developed originally by AI Singapore and maintained by the community. It runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux. It allows automating web browsers, desktop apps, keyboard/mouse actions and supports both visual (image-based) and DOM-based automation.
Best for: Users who want simple, cross platform automation of web or desktop tasks without heavy coding.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Natural-language syntax: Enables writing automation flows in readable, human-like commands.
- Cross-platform and visual automation: Automates tasks on Windows, macOS, Linux and supports visual recognition plus DOM-based UI actions.
- Integration with scripting and data tools: Works with Python, R or JS for advanced data handling or scripting needs.
Verdict: Simple cross-platform RPA tool; limited debugging and advanced test capabilities.
10. Axiom.ai
Axiom.ai is a no-code browser automation tool that uses a Chrome extension to automate web UIs by replicating user clicks, typing, navigation, and form entry. It supports data extraction, form filling, file uploads/downloads and works on web apps ranging from CRMs to marketplaces. It offers scheduling or webhook triggers for tasks.
Best for: Business users or small teams that need no-code automation for routine web tasks.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Visual web scraping: Extract structured data without writing code.
- Form and data entry automation: Automates repetitive form filling and data submission.
- Flexible triggers and scheduling: Runs bots manually, on a schedule, or via webhooks/Zapier.
Verdict: Efficient no-code web automation tool for business tasks, but less reliable for complex flows.
11. UiPath Studio Web
UiPath Studio Web is part of a full-stack RPA platform supporting browser automation through UI automation activities. It lets users build web automations via drag-and-drop or low-code flows, covering navigation, authentication, data scraping, form filling, and integration with other services and APIs. It supports Chrome, Edge and Safari browsers.
Best for: Enterprises or teams needing browser automation integrated within wider business workflows.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Cross-browser UI automation: Works on Chrome, Edge, and Safari with extension support.
- Drag-and-drop builder: Lets non-coders build automation flows quickly.
- Enterprise-grade integration & orchestration: Connects browser automation with backend processes, APIs, and document workflows.
Verdict: Enterprise-grade automation tool with integrations, however it feels heavy for small or quick tasks.
12. Bardeen
Bardeen is a browser extension built for productivity automation with focus on web apps and SaaS tools. It automates repetitive web tasks such as data export/import, form filling, CRM updates, data transfers, and can trigger workflows based on schedules or events. It aims to help users automate routine browser workflows quickly.
Best for: Individuals or teams that rely on SaaS apps and want to automate routine browser-based operations.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Extension-based automation: Runs directly inside the browser without separate installation overhead.
- Workflow templates for common tasks: Offers prebuilt automation flows for popular web tasks.
- SaaS integration: Works well with cloud tools such as CRMs, spreadsheets, dashboards for workflow automation.
Verdict: Good for daily browser tasks and productivity flows in SaaS-heavy workflows. But lacks depth for structured testing or complex automation scenarios.
13. Microsoft Power Automate
Microsoft Power Automate is a broad automation platform that supports browser automation through its UI flow (RPA) features plus connectors to many services. It can record browser interactions, automate legacy web apps, and integrate with APIs, Microsoft services, and third-party tools. It supports both attended and unattended flows and works on desktops or cloud agents.
Best for: Organizations already in the Microsoft ecosystem seeking cross-application automation including browsers and business apps.
Key Features and Benefits:
- UI flows for web automation: Records and plays back clicks, typing and UI actions on web pages.
- Large connector ecosystem: Links web automation with email, database, cloud apps, and enterprise services.
- Support for legacy apps and modern web apps: Automates both API-based and UI-only applications in one platform.
Verdict: Ideal for broad business process automation, however it is weak for fine-grained browser tests.
How to Choose the Best Browser Automation Tool
Selecting the best browser automation tool requires evaluating multiple criteria to match testing needs, team skills, and infrastructure. Below are key considerations with edge-case examples:
- Browser and device coverage is essential for catching issues across real environments. Without it, problems like a form breaking only on Safari 13 on an older iPhone go unnoticed.
- Test stability matters when dealing with dynamic pages. Tools need to handle async content, otherwise scripts fail when elements-like a button that appears only after an API call-load late.
- Execution speed and parallelism determine how quickly teams can validate changes. Without parallel runs, large suites (e.g., 300 tests) can take hours and delay releases.
- CI/CD integration ensures tests run automatically across branches and environments. Tools that lack this require manual execution and slow down deployment pipelines.
- Strong debugging tools help teams quickly isolate failures. Without logs or videos, issues like a dropdown failing only in Firefox 91 become difficult to reproduce and fix.
- Low maintenance and infrastructure overhead reduce disruptions. Cloud tools that auto-handle browser updates prevent scenarios where a new version breaks multiple scripts.
- Security and compliance are critical for teams testing behind firewalls. Without secure tunneling, tools can’t access private staging or internal environments.
BrowserStack Automate meets all these requirements by providing real devices, parallel execution, detailed debugging, seamless CI/CD integration, and automatic infrastructure management.
Best Practices of Using Browser Automation Tool
Choosing the best browser automation tool is only the first step. For maximum reliability, speed, and consistent results, follow the best practices outlined below:
- Use stable selectors: Select elements with IDs or>Run tests in parallel: Execute multiple tests at once to shorten execution time and provide faster feedback for development cycles.
- Test on real browsers and devices: Validate scripts on actual devices and browsers to detect environment-specific issues missed by emulators.
- Keep tests small and atomic: Break tests into smaller units to isolate failures and simplify maintenance for long-term reliability.
- Record detailed logs: Capture screenshots, console outputs, and network activity to diagnose failures quickly and reduce debugging effort.
- Apply retries only for transient issues: Retry tests only for network or temporary errors to avoid masking genuine bugs in automation suites.
- Prioritize critical tests: Run high-priority tests first in pipelines to catch major regressions early and optimize test execution.
- Review and update tests regularly: Periodically clean obsolete scripts, update selectors, and optimize workflows to maintain stability and accuracy.
Conclusion
Browser automation has become essential for modern web testing and workflow efficiency. It reduces manual effort, ensures consistency, and speeds up release cycles. However, challenges like cross-browser inconsistencies, flaky scripts, dynamic UIs, and limited device coverage often slow teams down. Selecting the right tool is critical to overcome these hurdles.
BrowserStack Automate addresses these challenges, eliminates infrastructure overhead, and delivers accurate results across diverse environments. Schedule a consultation with our experts to learn how it can simplify your automation workflows and improve testing efficiency.