Modern applications evolve rapidly, with frequent layout, color, and component updates.
Even a minor CSS change can shift a button, hide a label, or affect contrast, issues that functional tests often miss.
Overview
What is Visual Comparison Test?
A visual comparison test automatically compares UI screenshots across builds to spot unintended design changes like layout shifts, color mismatches, or broken elements. This ensures consistent visuals across browsers and devices. Tools like BrowserStack Percy make this process faster, smarter, and more reliable.
How Visual Comparison Test Works:
- Capture Screenshots: Take snapshots of the UI at defined states.
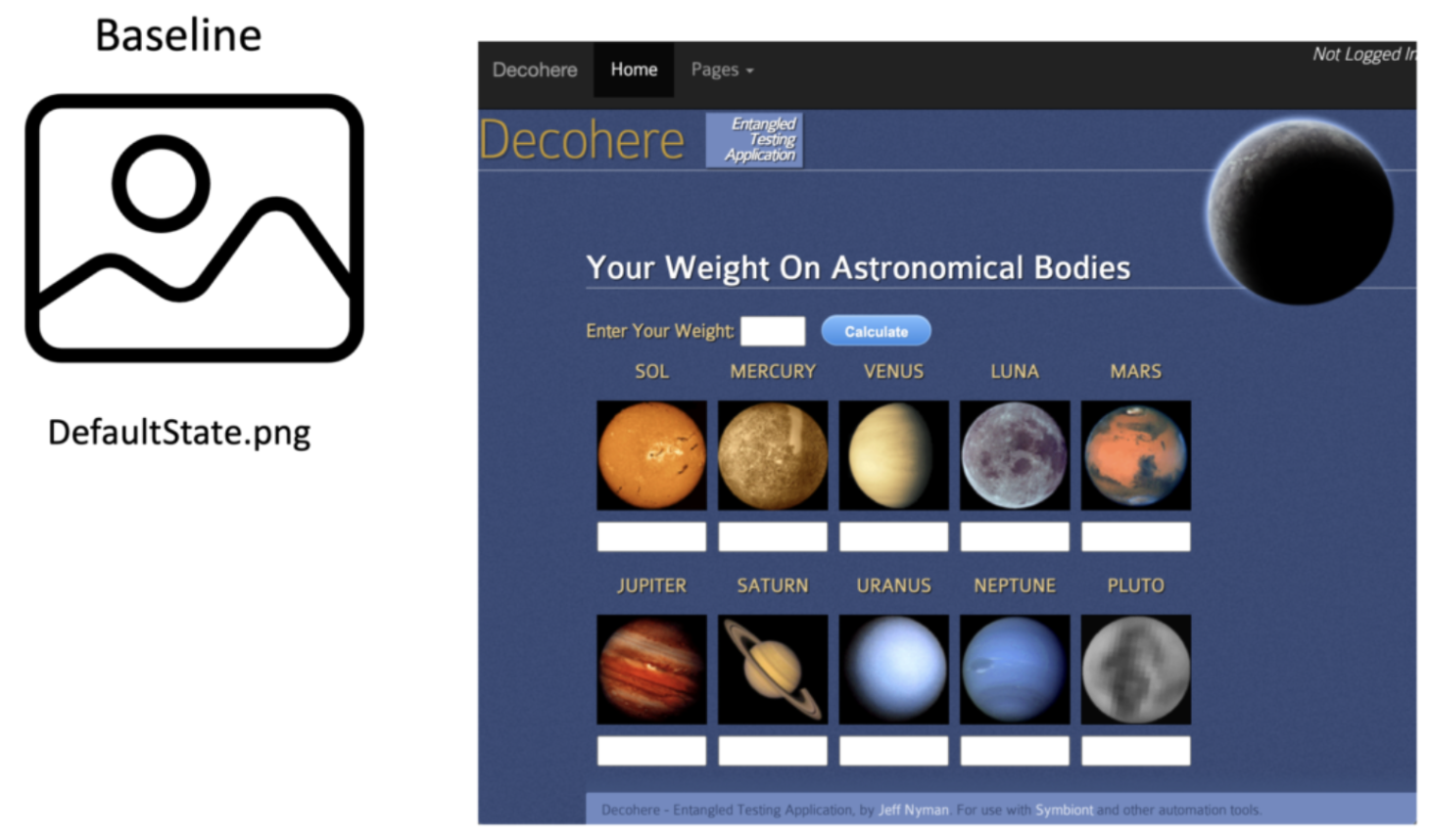
- Set Baseline: Save the initial UI images as the reference.
- Compare Builds: Capture new screenshots after changes and compare them with the baseline.
- Detect Differences: Identify visual shifts like spacing, color, or layout issues.
- Review Results: Highlight and review visual diffs to approve or fix changes.
This guide explores what a visual comparison test is, how it works, where it’s applied and the tools that simplify it.
What is a Visual Comparison Test?
A visual comparison test is a technique used to check whether a web page or application looks the same after changes in code, style or content. It captures screenshots of the current user interface and compares them with an approved reference image called a baseline. Any visual differences between the two are automatically highlighted for review.
This testing method focuses on how an application appears to users, rather than how it functions. It helps identify subtle visual shifts, misplaced elements and design inconsistencies that normal functional or automation tests might overlook.
By automating these comparisons, teams can quickly verify design stability across browsers, devices and screen sizes. Modern tools such as BrowserStack Percy, make this process reliable, repeatable and easy to include in continuous testing pipelines.
Use Cases of Visual Comparison Tests
Visual comparison testing is applied whenever maintaining the visual accuracy of an interface is critical. It detects UI-level issues that traditional tests may miss. Below are six practical and common use cases:
- Layout validation: Identifies shifted buttons, misaligned text or broken layouts after CSS or component changes.
- Cross-browser consistency: Detects visual differences in rendering across Chrome, Firefox, Safari or Edge.
- Responsive design verification: Ensures pages display correctly on mobile, tablet and desktop resolutions.
- Brand and theme assurance: Confirms that fonts, colours and design tokens remain consistent after design updates.
- Asset integrity check: Flags missing icons, incorrect fonts or broken images during build or deployment.
- Pre-release visual regression scan: Acts as a final checkpoint to prevent unintended visual changes before production releases.
Difference Between Visual Testing and Visual Comparison Testing
Although both aim to ensure visual accuracy, visual testing and visual comparison testing differ in purpose, coverage and execution. The table below outlines the key differences clearly and simply.
| Aspect | Visual Testing | Visual Comparison Testing |
| Purpose | Ensures that the user interface looks and functions correctly for end users. | Focuses only on comparing new UI visuals against a baseline to detect unintended visual changes. |
| Scope | Covers manual reviews, exploratory checks and usability validation along with design accuracy. | Limited to detecting differences in layout, colour, font, alignment or spacing. |
| Execution Type | Often manual or semi-automated through design reviews or exploratory tests. | Fully automated using snapshot or image-based comparison tools. |
| Automation Tools | May use frameworks like Selenium or Cypress for UI validation, combined with manual inspection. | Uses specialised tools such as BrowserStack Percy. |
| Output | Provides qualitative feedback about the overall look and user experience. | Produces visual diff images highlighting precise pixel-level differences. |
| Use Case Example | Checking button interactions, page navigation or dynamic element behaviour. | Detecting unexpected colour, alignment or layout shifts after CSS or code updates. |
How a Visual Comparison Test Works
A visual comparison test follows a simple, structured process. It captures screenshots of the user interface, compares them with a baseline and highlights any visual differences. This method is automated, repeatable and easy to integrate into CI/CD pipelines.
Below is the step-by-step process:
1. Set the Baseline: Capture initial reference screenshots of key UI pages or components to establish the visual standard for all future comparisons.
Example: Capturing the homepage layout after a major design release.
2. Apply Code or Design Changes: Developers update styles, features, or layouts and deploy the rebuilt application in a test environment.
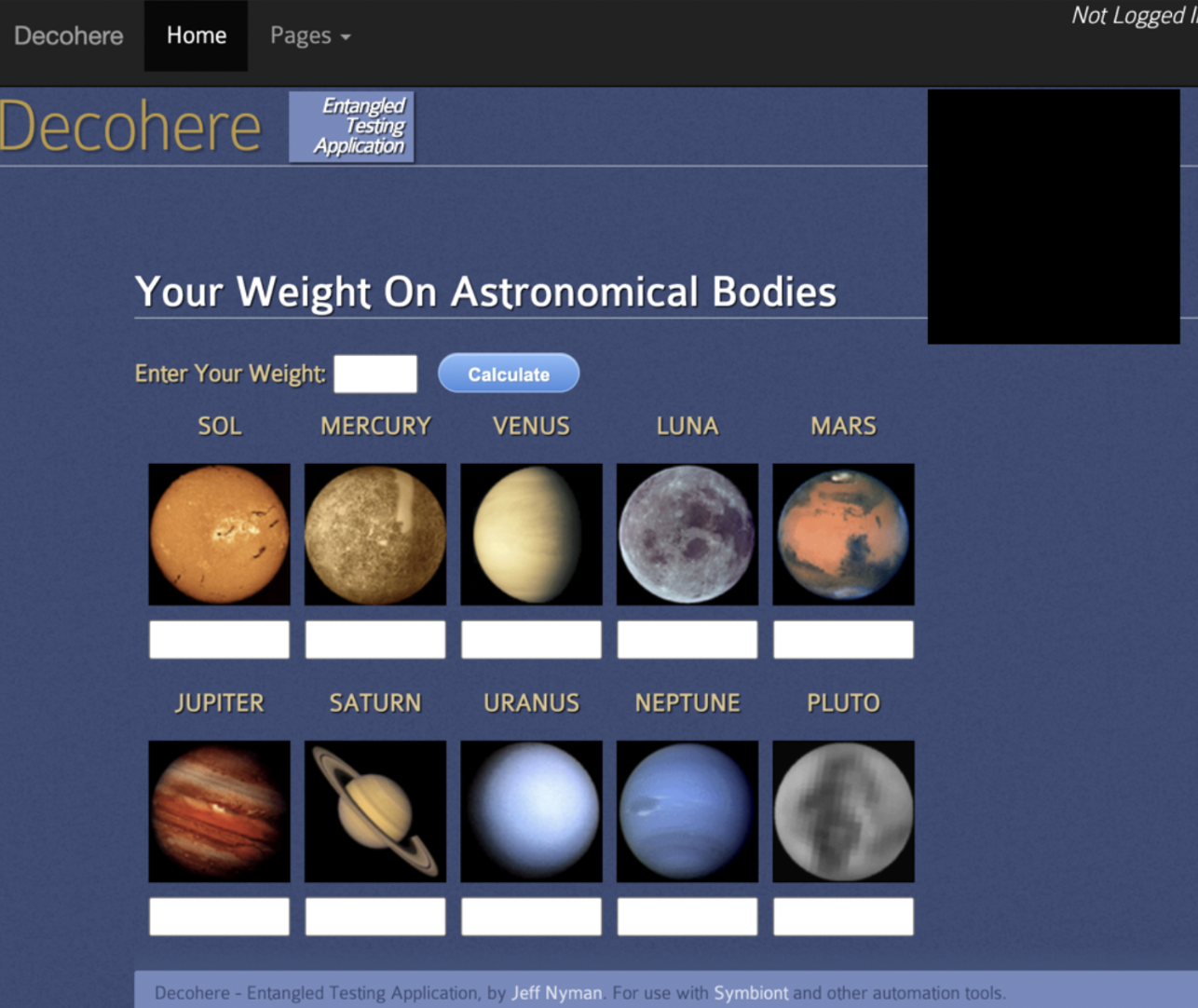
3. Capture New Screenshots: Automated scripts capture fresh screenshots across browsers and devices using tools like Playwright or BrowserStack Percy.
Example: Capturing the login screen across Chrome and Firefox to verify layout consistency.
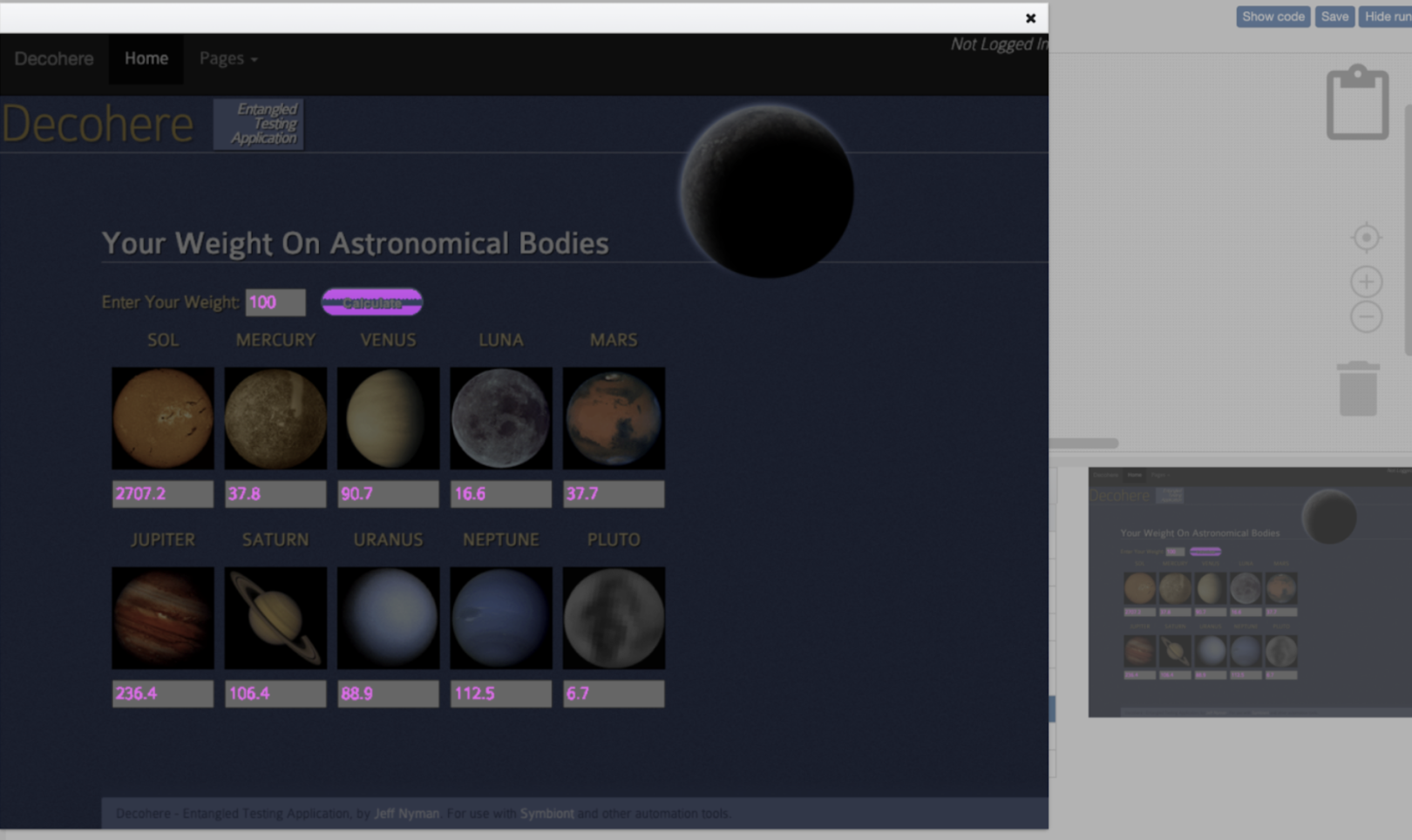
4. Compare with Baseline: The tool performs pixel-level comparison to highlight visual differences such as spacing, color, or alignment shifts.
Example: A colour mismatch in the header background is flagged as a diff for review.
5. Review Visual Diffs: Teams review highlighted changes, approving expected updates and logging unintended ones as defects.
Example: Percy’s dashboard highlights a button shift by helping testers quickly identify layout drift.
6. Update Baseline: Approved visuals are saved as the new baseline, maintaining an up-to-date visual reference for future tests.
Core Components of a Visual Comparison Test
A visual comparison test relies on several core components that work together to capture, analyse and report UI changes with precision.
- Baseline Image: Serves as the reference for comparison. Each new screenshot is matched against this approved baseline to detect layout or style differences.
- Automation Setup: Defines which pages or components to capture during tests. Frameworks like Playwright, Cypress or Selenium integrate with tools such as BrowserStack Percy to ensure consistent, repeatable runs.
- Screenshot Engine: Captures the latest UI state across devices and browsers using the same viewport and resolution for accuracy.
- Comparison Engine: Performs pixel-by-pixel analysis between the current and baseline images by flagging any visual drift automatically.
- Review Dashboard: Displays visual diffs for quick inspection by allowing testers to approve expected changes or report defects.
- CI/CD Integration: Embeds visual testing into pipelines like Jenkins or GitHub Actions, ensuring design validation happens with every build. Although both aim to ensure visual accuracy, visual testing and visual comparison testing differ in purpose, coverage and execution.
Learn More:Strategies to Optimize Visual Testing
Benefits of Performing Visual Comparison Tests
Visual comparison testing offers measurable advantages to both developers and QA teams by improving quality, speed and confidence in every release.
- Early Detection of Visual Defects: Automatically catches layout shifts, alignment errors or missing elements that functional tests might miss.
- Consistent User Experience: Ensures the interface looks identical across browsers, devices and screen sizes, maintaining a professional and trustworthy brand image.
- Reduced Manual Effort: Eliminates repetitive visual checks and manual comparisons, freeing testers to focus on exploratory and usability testing.
- Faster Feedback Cycles: Integration with CI/CD pipelines provides immediate visual validation after each build or commit.
- Higher Accuracy in Design Validation: Pixel-level comparison highlights even the smallest unintended changes by ensuring design fidelity.
- Better Collaboration Between Teams: Centralised dashboards make it easy for developers, designers and QA engineers to review and approve changes together.
- Improved Release Confidence: Continuous visual testing minimises UI regressions, enabling faster and more reliable deployments.
Learn More:Top 17 Visual Testing Tools in 2025
Popular Tools for Visual Comparison Testing
Modern visual comparison testing tools make it easier to automate screenshot capture, detect pixel-level differences and maintain visual consistency across builds. Below are some of the most widely used platforms that simplify and scale visual comparison testing.
1. BrowserStack Percy
Percy by BrowserStack is an AI-powered visual testing platform designed to automate visual regression testing for web applications, ensuring flawless user interfaces on every code commit.
Integrated into CI/CD pipelines, Percy detects meaningful layout shifts, styling issues, and content changes with advanced AI, significantly reducing false positives and cutting down review time for fast, confident releases.
- Effortless Visual Regression Testing: Seamlessly integrates into CI/CD pipelines with a single line of code and works with functional test suites, Storybook, and Figma for true shift-left testing.
- Automated Visual Regression: Captures screenshots on every commit, compares them side-by-side against baselines, and instantly flags visual regressions like broken layouts, style shifts, or component bugs.
- Visual AI Engine: The Visual AI Engine uses advanced algorithms and AI Agents to automatically ignore visual noise caused by dynamic banners, animations, anti-aliasing, and other unstable elements. It focuses only on meaningful changes that affect the user experience. Features like “Intelli ignore” and OCR help differentiate important visual shifts from minor pixel-level differences, greatly reducing false positive alerts.
- Visual Review Agent: Highlights impactful changes with bounding boxes, offers human-readable summaries, and accelerates review workflows by up to 3x.
- No-Code Visual Monitoring: Visual Scanner allows rapid no-install setup to scan and monitor thousands of URLs across 3500+ browsers/devices, trigger scans on-demand or by schedule, ignore dynamic content regions as needed, and compare staging/production or other environments instantly.
- Flexible and Comprehensive Monitoring: Schedule scans hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly, analyze historical results, and compare any environment. Supports local testing, authenticated pages, and proactive bug detection before public release.
- Broad Integrations: Supports all major frameworks and CI tools, and offers SDKs for quick onboarding and frictionless scalability.
App Percy is BrowserStack’s AI-powered visual testing platform for native mobile apps on iOS and Android. It runs tests on a cloud of real devices to ensure pixel-perfect UI consistency, while AI-driven intelligent handling of dynamic elements helps reduce flaky tests and false positives.
Pricing
- Free Plan: Available with up to 5,000 screenshots per month, ideal for getting started or for small projects.
- Paid Plan: Starting at $199 for advanced features, with custom pricing available for enterprise plan.
2. Applitools Eyes
Applitools Eyes is an AI-powered visual testing platform that intelligently compares application UIs across browsers, devices and operating systems. It uses machine learning based image analysis to detect genuine visual bugs while ignoring acceptable variations like browser rendering differences or minor anti-aliasing effects.
Key Features
- AI-Driven Visual Validation: Uses Visual AI to identify true UI changes, reducing false positives from minor pixel differences.
- Cross-Platform Support: Works seamlessly with Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, Appium and other automation frameworks.
- Ultrafast Grid Execution: Runs large visual test suites in parallel across browsers and viewports, speeding up feedback cycles.
- Comprehensive Dashboard: Centralises results for easier collaboration, baseline management and trend analysis.
Verdict
Applitools Eyes is good for enterprise teams needing advanced AI-based visual validation and large-scale test coverage. However, it cannot fully replace lightweight tools like Percy for quick visual checks or smaller development workflows that prioritise speed and simplicity.
Must Read: Applitools Alternatives for Visual Testing
3. Playwright Snapshot Testing
Playwright Snapshot Testing is an open-source feature within Microsoft’s Playwright framework that allows teams to capture UI snapshots during automated tests. It compares the current visual output against stored reference images to detect unintended visual differences by making it ideal for developers who want quick, code-driven visual checks.
Key Features
- Built-In Visual Comparison: Natively supports image and DOM snapshot testing without needing third-party tools.
- Cross-Browser Execution: Runs tests on Chromium, Firefox and WebKit, ensuring consistent visuals across major browsers.
- Code-Integrated Workflow: Let’s developers write, run and validate visual snapshots directly within their Playwright test scripts.
- Custom Thresholds and Masking: Offers fine-grained control over acceptable visual diffs and the ability to ignore dynamic elements.
Also Read: Snapshot Testing in iOS
Verdict
Playwright Snapshot Testing is good for developers who prefer open-source, code-level visual comparison within their automation suites. However, it cannot replace dedicated visual testing tools like Percy or Applitools, which provide richer dashboards, collaboration and CI/CD reporting capabilities.
4. Chromatic
Chromatic is a visual testing and review tool built by the creators of Storybook. It helps front-end teams automate UI validation at the component level by capturing and comparing visual snapshots of stories. Chromatic makes it easy to identify design changes early in the development process, especially in component-driven frameworks like React, Vue or Angular.
Key Features
- Component-Level Visual Testing: Captures snapshots of individual UI components from Storybook for precise visual validation.
- Automatic Version Tracking: Compares component states across commits to detect unexpected styling or layout changes.
- Collaborative Review Workflow: Provides visual diffs and commenting features so designers and developers can review updates together.
- CI/CD Integration: Connects seamlessly with GitHub, GitLab and Bitbucket to run tests automatically with each pull request.
Verdict
Chromatic is good for front-end teams using Storybook who need automated visual checks at the component level. However, it cannot replace broader, page-level visual testing tools like Percy for full end-to-end visual regression coverage.
5. Functionize
Functionize is an AI-powered test automation platform that includes advanced visual testing capabilities. It enables teams to run automated visual checks as part of functional and regression tests without writing complex scripts. Functionize uses machine learning to analyse visual changes intelligently by reducing false positives and improving test reliability.
Key Features
- AI-Enhanced Visual Detection: Identifies visual differences in layouts and elements with context-aware algorithms.
- Unified Functional and Visual Testing: Combines UI, functional and visual validations in one platform.
- Cloud-Based Execution: Runs tests at scale across browsers and environments using Functionize’s intelligent test cloud.
- Smart Maintenance: Automatically adapts tests to minor UI changes, minimising the need for manual updates.
Verdict
Functionize is good for enterprise teams seeking AI-driven, low-maintenance visual and functional testing in one platform. However, it cannot match the fine-grained visual diff accuracy and collaborative review features offered by specialised tools like Percy.
Must Read: Functionize Alternatives
6. TestGrid
TestGrid is a unified cloud-based testing platform that supports both functional and visual testing for web and mobile applications. It allows teams to perform visual comparison tests directly within their automated test workflows, helping identify visual regressions early across browsers, devices and operating systems.
Key Features
- Integrated Visual Testing: Captures and compares UI snapshots alongside functional tests, by detecting layout shifts and style inconsistencies.
- Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Support: Runs visual tests on real devices and browsers hosted in the TestGrid cloud.
- No-Code Automation: Enables testers to create and execute visual tests without complex scripting.
- CI/CD and Third-Party Integrations: Works with Jenkins, GitHub and other CI tools for continuous visual validation.
Verdict
TestGrid is good for QA teams looking for an all-in-one testing platform with both functional and visual testing capabilities. However, it cannot offer the same depth of visual diff analysis and AI-based detection that specialised tools like Percy provide.
7. DevAssure
DevAssure is an AI-powered testing platform that supports both functional and visual testing. Its Visual Testing module automatically compares screenshots against baselines to detect colour, layout and design inconsistencies.
Key Features
- AI-Driven Visual Analysis: Detects subtle UI changes such as colour drift, element misalignment and spacing differences.
- Baseline Comparison System: Stores and updates reference images for consistent visual validation across builds.
- Advanced Masking and Filtering: Ignores dynamic or environment-based changes to minimise false positives.
- CI/CD Integration: Works with popular automation pipelines, allowing continuous visual validation during code updates.
Verdict
DevAssure is good for teams needing AI-supported, customizable visual comparison integrated into enterprise test environments. However, it cannot match the extensive ecosystem and scalability offered by established tools like BrowserStack Percy.
Common Challenges in Visual Comparison Testing
Visual comparison testing provides immense value but teams often face challenges that can affect accuracy and efficiency. Understanding these common issues helps in setting realistic expectations and designing better testing workflows.
- False Positives due to Dynamic Content: Elements such as timestamps, ads or animations can cause visual changes even when the layout is correct by leading to unnecessary alerts.
- Environment and Rendering Differences: Minor rendering variations between browsers, devices or operating systems can result in inconsistent screenshots and false diffs.
- Baseline Management: Maintaining accurate and updated baselines becomes difficult in large projects where frequent UI changes occur.
- Performance and Storage Overhead: Storing and processing multiple screenshots for each build can consume significant resources, especially in CI/CD pipelines.
- Limited Context in Diffs: Tools may highlight changes but not always explain why they occurred which requires manual investigation to confirm if the issue is valid.
- Collaboration Bottlenecks: Without proper dashboards or review workflows, multiple teams may struggle to approve or track visual changes efficiently.
Best Practices for Effective Visual Comparison Testing
Following structured best practices helps teams improve accuracy, reduce false positives and maintain consistent visual testing outcomes.
- Establish stable baselines: Capture reference screenshots only from verified, stable builds to ensure meaningful comparisons.
- Exclude dynamic content: Mask or ignore changing elements such as ads, timestamps or animations that cause unnecessary visual diffs.
- Maintain environment consistency: Run visual tests in identical browser, OS and viewport configurations to avoid rendering variations.
- Integrate visual tests early in CI/CD: Embed visual checks alongside unit and functional tests to catch regressions before deployment.
- Regularly update baselines: Refresh baseline images whenever intentional design changes are implemented.
- Use collaboration-friendly tools: Choose platforms that support visual diff dashboards, review workflows and approval systems for smoother team communication.
Conclusion
Visual comparison testing has become an essential practice for maintaining consistent user interfaces in fast-changing development environments. By comparing UI snapshots against reliable baselines, teams can detect unintended visual regressions long before release.
Modern tools such as BrowserStack Percy makes this process faster, automated and easier to integrate into CI/CD pipelines. When combined with best practices like stable baselines, collaboration and environment control, visual comparison testing ensures every build looks as intended across browsers and devices.
In essence, it bridges the gap between design accuracy and functional reliability, helping teams deliver visually flawless digital experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary goal of conducting a Visual Comparison Test?
The primary goal of a visual comparison test is to ensure that the user interface looks exactly as intended after any change in code, design or content. It helps detect unexpected visual differences such as alignment issues, missing elements or colour mismatches that functional testing might miss.
2. When should a development or quality assurance team consider implementing a Visual Comparison Test?
Teams should implement visual comparison testing when UI consistency becomes critical, especially during frequent design updates, responsive layout adjustments or multi-browser releases. Introducing it early in the CI/CD process ensures that every visual element remains consistent and error-free across versions.